iversification quickly and efficiently.
00:00:11 – 00:00:30
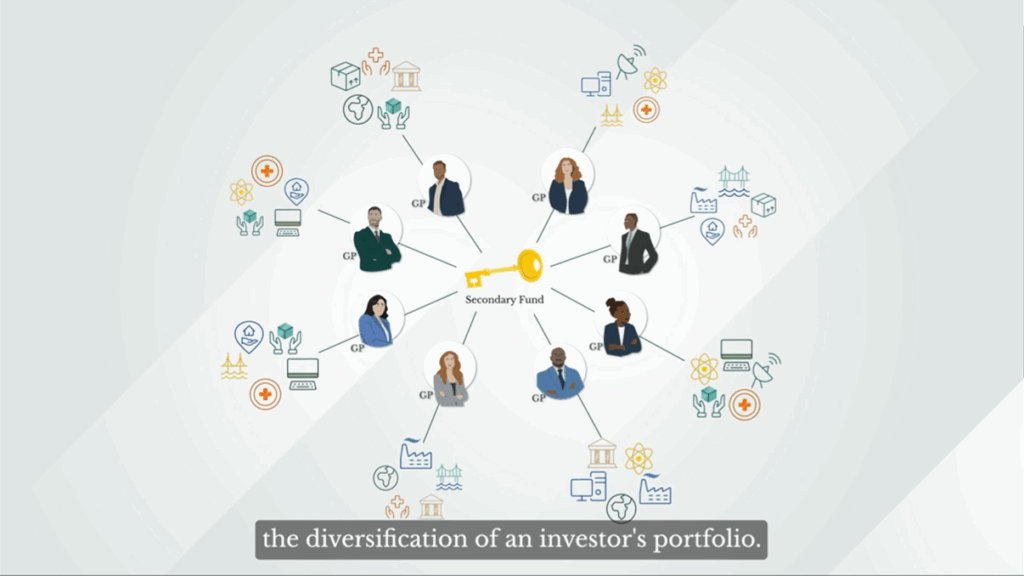
In a typical primary private equity fund, a manager or GP typically invests in a concentrated portfolio of companies over the fund’s ten-year life. By contrast, a single investment in a secondary fund can offer instant exposure to a broad mix of primary private funds and underlying companies.
00:00:31 – 00:00:53
This illustrates the potential scale of diversification that can be achieved by investing in a secondary fund. Furthermore, it’s not uncommon for a single secondary fund to have exposure to hundreds of general partners and thousands of underlying companies. This breadth of exposure significantly enhances the diversification of an investor’s portfolio.
00:00:55 – 00:01:04
Depending on what type of secondary investment you make, whether it be a drawdown or evergreen fund structure, the diversification changes over the life of the fund.
00:01:04 – 00:01:28
In a typical ten-year drawdown fund, diversification declines over time as underlying investments are gradually sold, and proceeds are returned to investors. Conversely, an evergreen fund, also known as a perpetual fund, continuously reinvests proceeds into new deals, helping to maintain diversification while also providing investors with regular distributions.
00:01:28 – 00:01:37
Because of their ability to provide broad diversification and reduced volatility, secondary investments can play a key role in building a well-balanced portfolio.
00:01:38 – 00:01:56
While private market investing offers great potential, it’s important to recognize that it can be complex and carries risks. Partnering with a manager who has a proven track record and expertise in navigating diverse market conditions is essential for success in this growing segment of the investing landscape.